In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, supply chain management has emerged as a critical component for organizations seeking to stay competitive. Traditional supply chain systems often suffer from slow processes, errors, a lack of transparency, and fragmented data across multiple participants. The adoption of blockchain in supply chain and logistics opens up new ways to tackle these challenges and build more resilient, data-driven operations.
In this article, we explore how blockchain in supply chain management works in practice, what benefits it brings, and where it delivers the most value. You will see how blockchain for supply chain improves transparency, product traceability, and coordination between multiple partners — from raw material suppliers and manufacturers to distributors and retailers. We will also look at real blockchain supply chain use cases and answer how blockchain is used in supply chain today and what to expect in the future.
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions transparently and immutably. Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain operates on a distributed network of computers known as nodes, where each node has a copy of the entire ledger. This decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks or third-party verification systems, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced costs.
Blockchain’s key features include security, transparency, and immutability. Transactions, once recorded on the blockchain, cannot be altered or tampered with, ensuring data integrity. The transparency of blockchain allows all participants in the network to view and verify transactions, fostering trust and eliminating the need for blind reliance on intermediaries.
To ensure the security of transactions, blockchain utilizes cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction in a chain, creating a secure and tamper-resistant record. Consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake, validate and verify transactions, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the ledger.
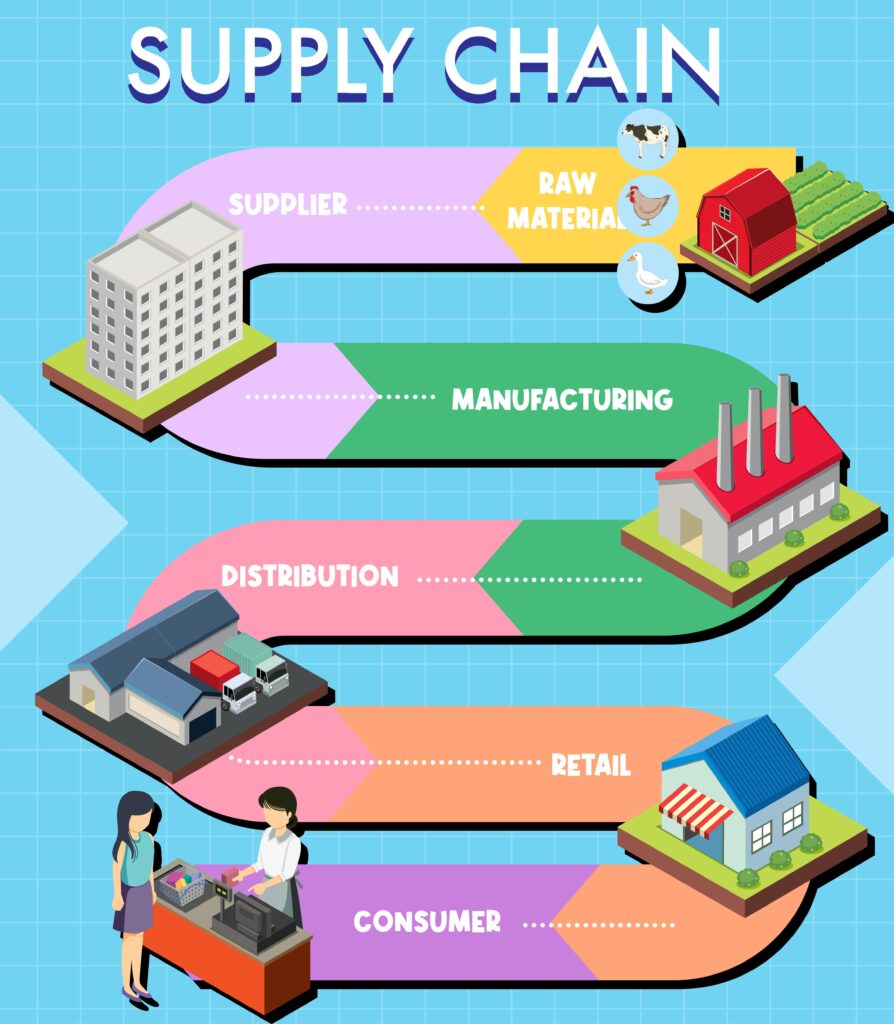
Supply chain management (SCM) refers to the coordination and oversight of all activities involved in the production, procurement, transformation, and distribution of goods and services from their origin to the end consumer. It encompasses the entire network of organizations, resources, technologies, and processes that collaborate to deliver products or services to customers.
The primary objective of supply chain management is to optimize the flow of goods and information across the supply chain, ensuring the right product is delivered to the right place, at the right time, and at the right cost. Effective supply chain management involves strategic planning, efficient execution, and continuous monitoring of various interconnected activities such as sourcing, procurement, production, inventory management, transportation, and customer service.
By streamlining and integrating these processes, organizations can achieve numerous benefits, including cost reductions, improved customer satisfaction, enhanced operational efficiency, increased agility, and better risk management. Supply chain management plays a vital role in enabling companies to respond to market demands, minimize disruptions, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business environment.
Supply chain management (SCM) faces a multitude of challenges in today’s complex business landscape. These challenges can hinder the efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness of supply chain operations. Understanding and addressing these challenges are crucial for organizations to optimize their supply chains and gain a competitive advantage.
One major challenge is the need for a universal database that encompasses all relevant information across the supply chain. This lack of centralized data leads to information gaps and inefficiencies, making it difficult to track and trace products accurately.
Traceability of assets throughout the supply chain is critical for ensuring product authenticity, quality control, and compliance. However, many supply chains struggle with incomplete or inconsistent traceability systems, making it challenging to identify the origin, journey, and current status of products.

Supply chains often incur unnecessary costs due to factors such as inefficient inventory management, excessive transportation expenses, and suboptimal procurement processes. These costs can significantly impact the bottom line of businesses.
Quality analysis is vital to ensure product conformity and meet customer expectations. However, lengthy and complex quality analysis procedures can result in delays in the supply chain, leading to customer dissatisfaction and potential revenue loss.
Rapidly changing customer demands and preferences pose a challenge for supply chain management. Organizations must strive to align their supply chains with evolving customer expectations, such as fast delivery, customization options, and sustainable practices.
Integrating supply chain management systems with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) and other business systems can be complex. A lack of seamless integration can lead to data silos, manual workarounds, and limited visibility across different departments and processes.
As supply chains become more digitized and interconnected, they become vulnerable to cybersecurity threats and data breaches. Protecting sensitive supply chain data and ensuring data privacy are critical concerns that need to be addressed effectively.
Scalability is a challenge when supply chains need to handle increased volume, complexity, or geographical expansion. Scaling supply chain operations while maintaining efficiency and flexibility requires careful planning and robust infrastructure.
Compliance with various legal and regulatory requirements adds complexity to supply chain management. Changing regulations and differing standards across regions or industries can create compliance challenges and the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Managing supply chains involves making cost-effective decisions at every stage. Balancing cost considerations while ensuring quality, sustainability, and customer satisfaction can be a delicate task.

Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing a decentralized, transparent, and secure platform for tracking and verifying transactions. In the context of the supply chain, blockchain acts as an immutable ledger that records and stores information about the movement of goods, transactions, and other relevant data across the supply chain network.
By utilizing blockchain, supply chain stakeholders can have real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, from the sourcing of raw materials to the delivery of the final product. The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation, enhancing trust and accountability among participants.
Blockchain’s key features, such as immutability, transparency, and cryptographic security, enable reliable traceability of products, authentication of their origin, and validation of their quality. Smart contracts, programmable agreements stored on the blockchain, can automate and enforce compliance with predetermined conditions, streamlining processes and reducing manual errors.
Before diving into detailed benefits, here is a simple overview of why blockchain in supply chain management is so powerful:
Below, we take a closer look at the key benefits of blockchain in supply chain management.
Blockchain enables real-time tracking of products as they move through the supply chain. Each transaction or transfer of goods is recorded on the blockchain, creating an immutable and transparent record of their journey. This allows stakeholders to track the status and location of goods in real time, leading to improved inventory management, reduced delays, and enhanced responsiveness to customer demands.
Traditional supply chain processes often involve complex and time-consuming paperwork, manual reconciliation, and communication delays between various parties. Blockchain streamlines these processes by automating documentation, verification, and authentication through smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that trigger predefined actions when specified conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing processing time significantly.
Traceability is crucial in supply chain management to ensure product authenticity, quality control, and compliance with regulations. Blockchain provides an auditable and transparent trail of all transactions and transfers, enabling end-to-end traceability. This helps identify the origin of raw materials, track the movement of products, and verify the authenticity and quality of goods. In industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, blockchain-powered traceability can enhance safety, reduce counterfeiting, and enable faster recalls.
Blockchain’s transparency and traceability contribute to building trust and fostering healthy customer relationships. With blockchain, customers can access accurate and verifiable information about the products they purchase, such as the origin, manufacturing processes, and certifications. This transparency boosts consumer confidence, increases brand loyalty, and facilitates ethical consumer choices.

By streamlining processes, reducing intermediaries, and enhancing efficiency, blockchain can lead to a higher return on investment (ROI) for businesses. Supply chain operations become more cost-effective as blockchain eliminates the need for manual reconciliation, reduces paperwork, minimizes errors, and optimizes inventory management. Additionally, faster processing and real-time tracking enable quicker order fulfillment, reducing lead times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Blockchain technology brings transparency to supply chain operations by providing a shared and immutable ledger visible to all authorized participants. This transparency fosters trust, accountability, and collaboration among stakeholders. Participants can view and verify transactions, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of data. Supply chain partners can access shared information, improving coordination, reducing disputes, and enabling more efficient decision-making.
Blockchain’s immutability ensures that once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or tampered with. This feature enhances data integrity, reducing the risk of fraud, counterfeiting, or manipulation of supply chain records. Immutability provides a high level of trust and reliability in the supply chain, making it resistant to data breaches or unauthorized changes.
Blockchain operates on a consensus mechanism where multiple participants in the network validate and agree on the accuracy of transactions. This decentralized consensus ensures that all parties involved have a shared view of the supply chain, eliminating the need for a central authority. Consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake provide a secure and trustworthy validation process for transactions, ensuring the integrity of the supply chain data.

In the food industry, blockchain helps improve safety and transparency by making every step of the journey traceable — from farm to table. Large retailers and producers use blockchain-based platforms to quickly identify the source of contaminated products during foodborne illness outbreaks. This reduces the scale of recalls, protects consumers, and restores trust more quickly.
Counterfeit drugs are a serious problem that cost billions and put lives at risk. By tracking each step of a medicine’s journey — from production to distribution and final delivery — blockchain in the pharma supply chain ensures that only genuine products reach pharmacies and patients. This makes the drug supply chain safer and more reliable.
High-end brands use blockchain to verify the authenticity of luxury products such as watches, handbags, and jewellery. Each item gets a unique digital record on the blockchain. By scanning a code, customers can see the history of the product, including where it was made and how it moved through the supply chain. This helps fight counterfeiting and strengthens customer trust.
Blockchain enables end-to-end visibility and traceability of goods, facilitating real-time tracking and monitoring of products at every stage of the supply chain. It eliminates the reliance on centralized intermediaries and manual paperwork, reducing delays, errors, and costs. Smart contracts on the blockchain automate and enforce contractual agreements, ensuring timely payments, and streamlining logistics processes.
Blockchain can streamline supply chain operations by eliminating intermediaries, reducing paperwork, and automating processes. Smart contracts on the blockchain enable self-executing agreements, ensuring timely payments, and reducing administrative costs associated with manual reconciliation.
Product recalls are a significant concern in industries such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, and food. Blockchain’s traceability feature allows for faster and more accurate identification of affected products, enabling targeted recalls and minimizing the financial and reputational damage associated with widespread recalls.
Counterfeit products pose a significant threat to industries like luxury goods, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. By implementing blockchain, supply chain participants can ensure product authenticity through immutable records of every transaction and transfer, reducing the risk of counterfeit items entering the supply chain.
Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency and accountability, enabling businesses to ensure ethical sourcing and production practices. By recording information about suppliers, certifications, and audits on the blockchain, organizations can verify compliance with ethical standards, such as fair trade or sustainability.

Blockchain’s real-time tracking capabilities provide end-to-end visibility into the movement of goods, optimizing logistics and supply chain processes. Participants can track shipments, monitor temperature and humidity conditions, and automate customs clearance, leading to improved efficiency and reduced delays.
Blockchain facilitates secure and transparent supplier payments. Smart contracts can automatically trigger payment once predefined conditions are met, such as successful delivery or quality verification. This reduces payment disputes, speeds up cash flow, and enhances trust between buyers and suppliers.
Blockchain can enhance food safety by enabling end-to-end traceability of food products. By recording every step of the supply chain, including origin, processing, and distribution, blockchain helps identify the source of contamination in case of foodborne outbreaks, enabling targeted recalls and preventing further harm to consumers.
Blockchain can facilitate efficient post-sale services by storing product information, warranties, and maintenance records on the blockchain. This enables manufacturers, service providers, and customers to access accurate and verifiable product histories, ensuring timely and effective post-sale support.
The oil and gas industry involves complex supply chains spanning multiple stages, from exploration to distribution. Blockchain can improve transparency, track oil ownership, streamline transactions, and enhance regulatory compliance, reducing fraud and enabling efficient supply chain management.
Blockchain can address challenges related to diamond provenance, certification, and authenticity. By recording the history of each diamond on the blockchain, from mining to cutting to retail, stakeholders can ensure the integrity of the supply chain and reduce the risk of conflict diamonds or fraudulent practices.
Blockchain technology can optimize the wine supply chain by providing visibility into the production, transportation, and storage of wines. This enables wine producers, distributors, and retailers to trace the origin, quality, and authenticity of wines, improving trust and reducing the risk of counterfeit products.
The pharmaceutical industry faces challenges related to drug counterfeiting, supply chain visibility, and regulatory compliance. Blockchain can address these issues by ensuring the traceability of drugs, preventing counterfeit products, and providing an auditable record of transactions and certifications.
Below are 15 companies that already use blockchain in their supply chains — from retailers and food producers to logistics providers and luxury brands.

Walmart has been at the forefront of blockchain implementation in the supply chain. By partnering with IBM, they developed a blockchain platform that allows for end-to-end traceability of food products. This enables Walmart to quickly identify the source of contaminated products during food recalls, enhancing consumer safety.
Brilliant Earth, a jewelry company, leverages blockchain technology to ensure the ethical sourcing of diamonds. By utilizing blockchain, they provide customers with a transparent and immutable record of a diamond’s journey, from mining to sale, ensuring the authenticity and ethical standards of each piece.
Bumble Bee Seafoods, a major seafood producer, uses blockchain to enhance traceability and transparency in its supply chain. By recording key information about the fish, including origin, catch location, and processing details, on the blockchain, Bumble Bee Seafoods ensures the integrity of its products and improves consumer trust.
IBM Food Trust is a blockchain-based platform that connects various stakeholders in the food industry, enabling end-to-end supply chain visibility and traceability. Participants can track and verify the origin, quality, and safety of food products, improving food safety and reducing fraud.
Ambrosus utilizes blockchain technology to improve supply chain transparency and integrity in the pharmaceutical, food, and luxury goods industries. Their platform enables real-time monitoring of products, ensuring compliance with regulations and enhancing trust among supply chain participants.

VeChain specializes in supply chain management solutions powered by blockchain technology. Their platform provides transparency and traceability for a wide range of industries, including logistics, food, and luxury goods. VeChain’s technology enables businesses to verify the authenticity and quality of products throughout the supply chain.
Provenance is a blockchain platform that enables businesses to track and trace products, ensuring transparency and ethical sourcing. They have successfully implemented blockchain solutions in industries such as fashion, seafood, and coffee, empowering consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase.
ChainLink is a decentralized oracle network that connects blockchain applications with real-world data and resources. In the supply chain context, ChainLink’s oracles provide secure and reliable data feeds, enabling smart contracts to interact with external systems and automate supply chain processes.
FedEx is exploring blockchain technology to enhance shipment tracking and reduce paperwork in the logistics industry. By integrating blockchain into their systems, they aim to improve supply chain transparency, reduce delays, and enhance customer satisfaction.

De Beers, the global diamond company, is piloting a blockchain platform called Tracr to track the journey of diamonds from mine to market. By recording each diamond’s unique identifier on the blockchain, De Beers ensures the authenticity and ethical sourcing of their diamonds.
Maersk, a leading global shipping company, partnered with IBM to develop TradeLens, a blockchain-based platform for the shipping industry. TradeLens provides end-to-end visibility and transparency in global trade, improving efficiency, reducing paperwork, and enhancing collaboration among supply chain stakeholders.
IBM has been actively involved in multiple blockchain supply chain projects, including collaborations with various industries to enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency. Their blockchain solutions enable secure and efficient data sharing, automating processes, and strengthening trust across supply chains.
Everledger is a blockchain-based platform that focuses on verifying and tracking high-value assets, particularly in the diamond and fine wine industries. By recording unique identifiers and relevant data on the blockchain, Everledger ensures the provenance, authenticity, and ownership history of these assets. This enhances trust, reduces the risk of fraud, and facilitates efficient transactions in these markets.

Carrefour, one of the largest retail chains globally, has implemented blockchain technology to enhance transparency and traceability in its food supply chain. Through their “Carrefour Quality Line” initiative, Carrefour leverages blockchain to allow customers to access detailed information about the production, quality, and sustainability of selected products by scanning a QR code. This empowers consumers to make informed choices and fosters trust in the food products they purchase.
Nestlé, a multinational food and beverage company, has partnered with OpenSC, a blockchain platform, to track the supply chain of milk from farms in New Zealand to Nestlé’s factories in the Middle East. This initiative aims to ensure the sustainability and ethical sourcing of milk, providing consumers with transparency and confidence in Nestlé’s dairy products.
The future of blockchain in supply chain management will depend on how quickly companies move from pilots to large-scale implementation. Today many projects are still in the proof-of-concept stage, but successful cases in food, pharma, logistics, and retail show that the technology can deliver measurable value.
Over the next few years, we can expect tighter integration between blockchain, IoT devices, and advanced analytics. Sensors and scanners will feed real-time data into blockchain networks, while AI will analyse this trusted data to predict disruptions, optimise routes, and improve inventory planning. This combination will make supply chains more resilient, responsive, and data-driven.
Industry-wide standards and interoperability will also play a key role. As more companies adopt blockchain in supply chain, consortia and platforms that enable secure data sharing between different organisations and systems will become increasingly important. Clearer regulations and guidelines for data privacy and digital identities will further accelerate adoption.
In the long term, blockchain supply chain solutions may change not only how products are tracked, but also how supply chain partners collaborate and share value. New business models based on tokenisation, outcome-based contracts, and circular economy initiatives will become more common as companies learn how to use blockchain to align incentives across the entire network.
Blockchain in supply chain management is no longer just a theory. Real projects show that it can provide end-to-end visibility, improve product traceability, reduce fraud and counterfeiting, and streamline complex logistics operations. When implemented correctly, blockchain for supply chain becomes a shared source of truth for all participants and helps companies make faster and more confident decisions.
At the same time, the technology is not a magic solution for every problem. Organisations still need to address challenges such as system integration, interoperability, governance, and change management. The most successful initiatives start with a clear business case, a limited but meaningful scope, and strong collaboration between business, IT, and external partners.
For companies that are ready to move forward, blockchain in the supply chain offers a way to build more transparent, resilient, and sustainable supply networks.
ND Labs can help you design and implement blockchain supply chain solutions tailored to your industry and operations, from discovery and architecture to development, integration, and support.
If you are considering a blockchain project in supply chain or logistics, feel free to contact our experts and discuss your ideas.